Introduction:
- Probiotics are live microorganisms (microbes) that can have beneficial effects on or inside any shrimp/fish/human being.
- Microorganisms that live within and help support bodily functions and health
- Biological approach for disease mitigation
Most common and recommended probiotics include:
- The Lactobacillus genus, including L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, L. casei and L. plantarum.
- The Bifidobacterium genus, including Bifidobacterium longum and Bifidobacterium breve
The 1990s saw the usage of antibiotics in aquaculture subsequently after scientific interventions the ban on antibiotics was implemented and the aquaculture community transformed itself and started the usage of probiotics which are the beneficial bacteria and has resulted in positive developments and became a primary method of preventing diseases. The development of probiotics for the higher vertebrates was studied in shrimps also and it was proved that probiotics are beneficial to shrimps in culture environment.
Benefits of probiotics:
• Improve key performance indicators associated with growth rates and feed utilization, stimulate the immunological responses and disease resistance in shrimps
• Probiotics can be supplemented in diet or culture media and positively affect the host through different mechanisms.
• Synthesis of several inhibitory compounds and competition with pathogenic bacteria for adhesion sites in the gut
• Modulation of the host’s immune responses, and the maintenance of the gut microbial balance
Selection criteria of probiotics:
• Adhere to host cells
• Exclude or reduce pathogenic adherence
• Stimulate the immunity of the host
• Persist and multiply
• Produce acids, hydrogen peroxide, and bacteriocins antagonistic to pathogen growth
• Be safe and therefore non-invasive, noncarcinogenic, and non-pathogenic
• Co aggregate and form a normal, balanced flora.
Life cycle of bacterial population:
It is important to understand the life cycle of bacteria so that it can be properly used for aquaculture. Once the bacteria are introduced into the culture environment, they tend to multiply in the way described in the 4 stages mentioned above in the graph depiction.
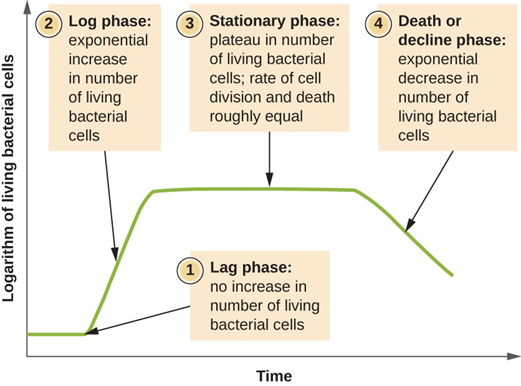
1. Lag phase: After introduction of the inoculum, they initially be constant and takes time to establish itself in the environment.
2. Log phase: This is the exponential phase where the bacteria multiply rapidly.
3. Stationary phase: During the stationary phase the bacterial cells are fully multiplied, and population becomes constant due to new cells formed equal to dead cells and maintaining the probiotic bacteria in the pond environment at this phase is important.
4. Death phase: During death phase the bacterial cells die rapidly decreasing the number of cells.
In the pond environment it will be essential to maintain the good probiotic bacterial population for which it has to be inoculated again so that their population do not decline following death phase.
Hence repeated application of probiotic bacteria into the culture pond environment is essential to get the beneficial effects of the bacteria. The application of prebiotics like the organic carbon source (like the juice made of Rice bran, GNOC, Yeast, Jaggery, curd etc.) in different forms helps to multiply the beneficial bacteria along with probiotic applications and prevents the bad vibrio from multiplying from the environment
How probiotics works in pond culture?
Aerobic bacteria such as Bacillus spp., used in probiotics like Aquacare Control and applied to pond water, help in the better functioning of the Nitrogen cycle, stabilizes the water quality by maintaining proper pH and alkalinity and help the shrimps thrive better in the pond environment by improving growth, survival and disease resistance.
A probiotic like Aquacare control should be used before stocking, especially after water treatment and during water colour preparation. The recommended dosage of Aquacare control before stocking is 4 x250g pouches per hectare (1 kg/ha) for 1 to 2 doses and during ongoing culture 2x250g pouches per hectare shall be applied once weekly.
Gut probiotics help the shrimp gut to be altered with the beneficial probiotic bacteria while using regularly and establishes in shrimp gut excluding the competitive bad bacteria. This in turn helps better digestion of feed, improves the growth and survival of shrimp and develops the defence mechanism of shrimp.
In case of the anaerobic bacteria usage, they help to sustain in the pond bottom sub surface area under anaerobic conditions and oxidises the Hydrogen sulphide formed due to accumulation of uneaten feed, and other wastes from the environment thereby helping better survival and growth of shrimp. The probiotics like Eliminator can be applied at 150 pellets per hectare weekly once during culture and the dosage can be doubled during challenging situations.
However, a probiotic cannot be used for treating a disease for one time and leaving it, but there should be a continuous usage of probiotics and prevent the disease challenges of shrimp. Also pond culture water when treated and developed before stocking leads to better establishment of beneficial bacteria in pond environment rather than applying the probiotic in untreated water used for culture ponds.
Conclusion:
Good farm management practices coupled with probiotic applications regularly would lead to successful harvests and better profitability for shrimp farmers.

